A Strategic Plan is a guiding framework for all types of organisations. It provides a clear vision and a set of priorities that are useful for a broad range of purposes, from day-to-day decision making, change management, growth strategies, seeking funding, and evaluating progress. The plan particularly helps by identifying goals and objectives with ways of achieving them, which can focus effort and volunteer time.
It is vital that committees are proactive rather than reactive in achieving goals and objectives. Without adequate planning, immediate issues tend to take up all available time. A strategic plan is a way to gain consensus – sharing and working towards a vision for the future which can develop cohesion among members. It can also help ensure committee governance responsibilities are met.
A strategic plan will also ensure organisations like sporting clubs continue to operate effectively and in a consistent direction despite personnel changes to the club committee and is a very important succession planning document. This is particularly important for junior sporting clubs in which parents of participants are often involved for short periods of time.
Planning process and stages
Developing a strategic plan is a significant and important undertaking. It can be helpful to develop a planning process to understand everything involved by considering the following:
The planning process should involve four to five key people within your committee and be led by the club president.
Club Structure
Before your organisation can start the planning process to establish a strategic plan, you will need to identify the current committee structure and locate your constitution.
Incorporated Associations are typically structured around a committee, which is responsible for administration, financial management, and governance.
The committee may include more roles depending on the size and operational requirements of the club. You may also have paid staff that may need to be involved and considered in the process.
Stage One – Organisational Data
All organisations should have a clear understanding of where they have come from and where they are now before any planning can be completed. Data allows the organisation to identify its current position to plan effectively for the future. Information to consider includes:
- Financial data
- Membership demographics
- Facilities needs/ arrangements in place
- Performance/ success stories/ awards
- Social activities
- Status of policies/ procedures
Stage Two- Environmental Scan

An ‘objective review’ of the current and anticipated environmental factors that impact your organisation. These include:
- Political
- Economic
- Demographic environment.
Think about who the stakeholders are, how they influence the organisation and what opportunities they present. Critical to this in sport is the peak body or organisation to which your club is affiliated.
Stage 3- SWOT analysis
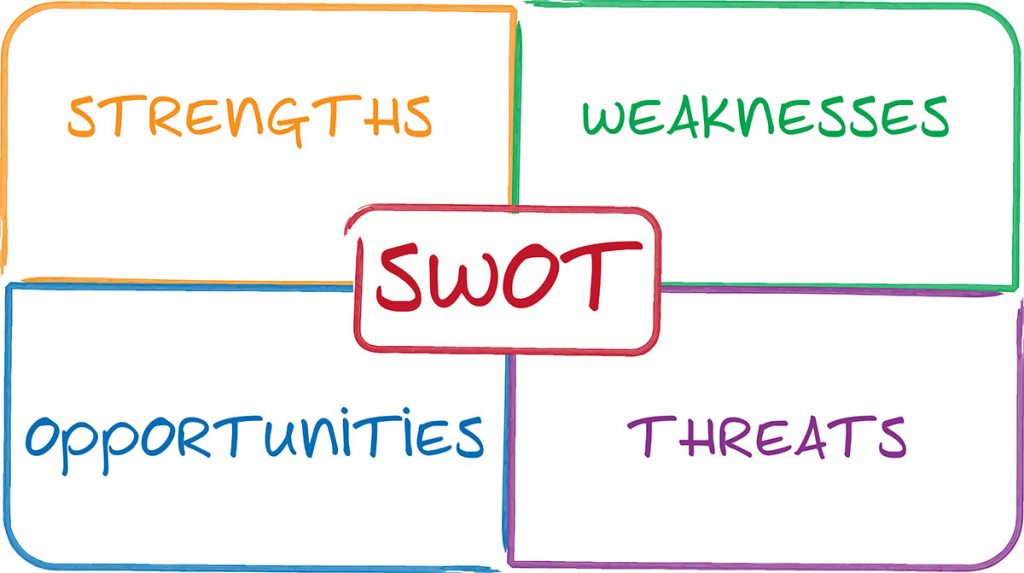
The SWOT analysis is the first step in determining the organisation’s priority areas for development. It will allow you to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats relevant to your club.
Strengths and weaknesses relate to the internal aspects of the club, such as facilities, members, coaches, volunteer resources, capacity and equipment.
Opportunities and threats are those external aspects relating to the organisation, such as funding, population changes, school/club link opportunities, and issues relating to weather, other sports codes, etc.

Stage 4 – Consultation
To help bring the club on the strategic planning journey, you need consultation and engagement with representatives across the organisation. This would include members, stakeholders volunteers, coaches, staff, and visitors. There is a range of ways to do this; through member surveys, workshops, interviews and the circulation of draft plans.
Stage 5- Develop Vision, Mission and Value Statements

A vision statement is a statement that states confirms what the organisation wants to achieve. A vision statement looks to the future and needs to be clear, concise, inspiring and challenging. You want to be able to achieve your vision within 5-10 years.
A mission statement clearly states what your organisation does and why it exists.
Where While your Vision vision is looking towards the future, your Mission mission is usually more practical, and action- orientated.
The mission statement answers the following questions:

- What is the organisation? (Its nature)
- What does it do? (Its products/services)
- Who does it serve? (Its customers)
- Why does it exist? (Its purpose)
Values state what your club believes in. Values are the core beliefs that shape the way people behave and make decisions. They provide a framework for how members treat one another and how they treat others such as potential members and stakeholders. Your value statements should reflect the culture wanted within your organisation.
Stage Six – Set Goals, Objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPI)
Goals, objectives and KPIs are an important part of any successful committee. They help determine how members make decisions and what activities they want to plan for. Goals are what the club wants to accomplish, objectives are the activities to achieve the goals, while KPIs are how objectives are measured. When determining goals, objectives and KPIs, consideration needs to be given to responsibilities, timelines and financial resources available.
Consider SMART goal setting principles when setting your goals:

Specific – be clear about what you want to achieve
Measurable – make sure the goal can be measured, and you can recognise if you’ve achieved your goal
Achievable – check that your goal is something you have the time, money and resources to meet
Relevant – ensure your goal is relevant to the direction you want your business to head in, for example, increasing profit, employing more staff, increasing brand awareness
Timely – set a realistic deadline for completing the goal.
For more information on strategic planning, contact michelle@gippsport.com.au






